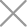
Size and Enclosure: DC MCCBs are typically larger, with enclosures made from materials like thermosetting Dough Molding Compounds (DMC) or flame-retardant Bulk Molding Compounds (BMC) with a V-0 rating, while DC MCBs are much smaller, with enclosures usually made from flame-retardant PA66 with a V-o rating.
Current Ratings: DC MCCBs generally have current ratings below 1600A, while MCBs have maximum current ratings below 125A. The difference in capacity means that DC MCCBs have wider application scenarios and accommodate thicker wires, sometimes reaching several hundred square millimeters, whereas DC MCBs are suitable for 50 square millimeters or less wires.
Mounting Methods:DC MCCBs are primarily installed using screws, which provide a secure and stable connection. MCBs are typically mounted on DIN rails. The different mounting methods make MCCBs more stable and easier to install compared to MCBs.
Product Lifespan: DC MCCBs have greater spacing between phases and incorporate arc extinguishing chambers, possessing stronger arc-extinguishing capability. They can withstand larger short-circuit currents and are less likely to cause phase-to-phase short circuits, resulting in a longer lifespan compared to MCB.
Application Fields: DC MCCBs are mainly used in industrial and large commercial electrical systems, while DC MCBs are commonly used in residential, small commercial, and light industrial applications, making them more suitable for installation in compact spaces.